4-1 Project Overview
Advanced Meter Infrastructure (hereinafter referred to as AMI) is one of the smart grid construction of Taipower, and the whole system is composed of modular intelligent electronic meter with computing and storage capabilities (hereinafter referred to as smart meters), communication systems for data transmission (hereinafter referred to as communication systems), and Meter Data Management System (hereinafter referred to as MDMS system) responsible for huge meter data management, storage, verification, and analysis(Figure 3).
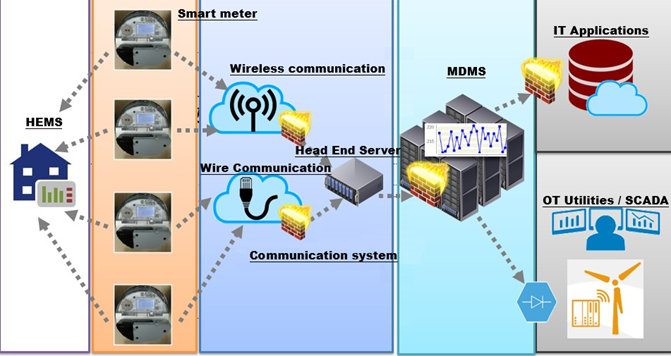
Figure 3 The system architecture of AMI in Taipower
In Taiwan, the high voltage (above 11.4KV) smart meters were completely installed in 2013 for users over 24,000. For the low-voltage users, up to the end of 2018, Taipower has achieved the smart meter establishment of 200,000 households and will attain the goal of 3 million households at the end of 2024. The following will be described for the planning, implementation, and management of AMI security protection.
4-2 Risk Assessment
For the security evaluation of the AMI system, Taipower has conducted the risk assessment on the use cases. Each use case was reviewed from a high-level, overall functional perspective which includes assets identification, vulnerabilities, threats and the specification of potential impacts. The output was used as the baseline for the selection of security requirements and the identification of gaps in guidance and standards related to the security requirements.
The risk assessment focuses on how meter data are handled through the AMI system end to end, from the smart meter to the MDMS system. Both the bottom-up and top-down approaches were used in performing the risk assessment. The bottom-up approach focused on well-understood problems that need to be addressed, such as authenticating and authorizing users or device to access the meter data, key management for meters, and intrusion detection for the MDMS system. In the top-down approach, logical interface diagrams were developed for the three functional areas (smart meter, AMI communication system, MDMS system) that are the major components of the AMI system. From the functional perspective, it is reviewed to see how the security measures shall be applied.
Taipower uses the methodology described above to evaluate the appropriate security measures that can be applied to the three major components of the AMI system. In Sec. 4.3 detail measures will be described.
4-3 Security Architecture of AMI
4-3-1 Smart Meter Security Protection Measures
The cover side of the smart meter has a seal point for seal lock to maintain the confidentiality of the meter data, avoiding illegal opening of the smart meter (Figure 4). From the outside of the smart meter, the data can only be transmitted through the optical communication port, and the optical communication port is designed according to the national standard of CNS 15593.
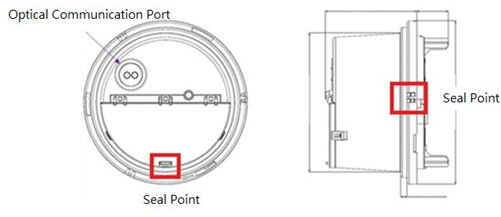
Figure 4 The Smart Meter Body Structure
In the smart meter acceptance test, Taipower has performed data reading and transmission testing, to ensure the integrity and availability of the meter data transmission. If the external cover of the smart meter is detected, the smart meter will immediately generate a “meter cover open” warning message and pass through the communication system back to the back-end system, in order to facilitate the proper event handled by Taipower personnel. The only way to reset “meter cover open” warning is through the back-end system or using the handheld device to send the reset instruction through the optical communication port. If the whole smart meter is disassembled, smart meter can still use the internal backup power to return “power outage” message to the back-end system in the case of loss of power, and since the entire disassembly of the smart meter will cause the household to lose power, the user will also report to the Taipower customer service system, whereby the dual reporting mechanism allows the personnel of Taipower to handle the abnormal event in time.
Smart meters are designed in accordance with the IEC 62056 standard, with a sound data transmission and confirmation mechanism to ensure the integrity of the meter data. Internal firmware, data and transmission operations are used in accordance with the NIST IR7268 standard of high-strength key technology for encryption processing. The smart meter has used different encryption key in the field area network (FAN, connected to AMI communication system), home area network (HAN, connected to the Home Energy Management System) and the local side, any reading or writing to the meter must use the correct key, otherwise the meter will not respond, to ensure the overall confidentiality of the meter software. The optical communication port of smart meter has the design of continuous retry times threshold, after a certain number of malicious accesses, internal security mechanism will initiate non-response, so as to avoid the possibility of violent cracking, to ensure the availability of meter system data. The smart meter also has a software security gateway to perform firewall function, flow control and log store for the FAN and HAN connection respectively.
4-3-2 Communication System Security Protection Measures
The transmission of meter data from the smart meter side is mainly through the telecommunications system, and use the fiber-optic line access to the Taipower Information Center. By using the VPN mode to separate the general public use of the Internet to ensure the AMI communication system security planning.
The security protection features of the AMI communication system are as follows:
- It shall have the security monitoring, incident or alarm reporting to protect the network.
- The transmission path in any part of the communication system shall be consistent with confidentiality, integrity (including data integrity and ACK mechanism), and reliability of secure two-way communication, to ensure the security of end-to-end communications.
- The encryption mechanism between devices must have at least AES-128 level or above, or in compliance with NISTSP 800-131A Specification.
- The communication system shall have encryption security management, store data encryption processing, software/firmware management, remote disconnect, equipment network management, and a backup system.
- Communication equipment should be remotely maintained and have security measures for permissions and password management to prevent unauthorized personnel from operating.
- It shall have the ability to protect against DDoS or man-in-the-middle attacks.
4-3-3 MDMS System Security Protection Measures
The MDMS system plays as the role of AMI data gatekeeper, Taipower has applied high safety standards to plan the relevant security measures, and should be in accordance with the laws released by the Executive Yuan of the ROC government, “Information System Classification and Security Protection Baseline Operation Provisions”, “Secure Software Development Process Guidelines “, “The Development of RFP Security RequirementsTemplate for Information System Outsourcing”, and other requirements that a high safety system should be compiled. The following will focus on the implementation of the relevant measures in the order of network boundary protection, internal network protection, host protection, application protection, and data protection.
- Network Boundary Protection
Based on the network perspective, the external connections of the MDMS system with the AMI communication systems and Intranet are equipped with the next generation firewall, and Intrusion Detection and Protection System (IDPS), in order to monitor incoming and outgoing traffic and network services in real time, and to avoid malicious access or blocking service attacks (such as DoS attacks).If it is necessary to have data transmission with the power system control system(OT system), the MDMS system shall use the one-way data diode to establish the connection, and the requirements of physical isolation can be achieved, so as to block the majority of intrusion and malicious attacks relying on the two-way communication scenario. MDMS system client service only provides general transaction operation functions, and for the development and maintenance operations (such as program version
updates, system management, and other system maintenance operations, etc.) must be operated through the monitored Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI), in order to reduce the likelihood of data leakage. The firewall, IDPS, unidirectional one-way data diode and VDI used in the MDMS system are certified by the international authority (such as Common Criteria EAL, FIPS 140-2 or NSS Lab, etc.)(Figure 5).
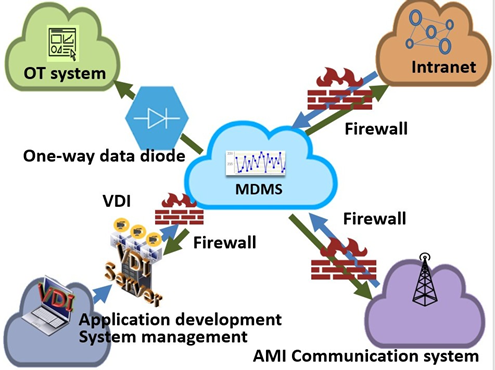
Figure 5 The MDMS system network boundary protection
Internal Network Protection For the data transmission related operations of the Internal network, the MDMS system fully adopts the Secure Communication Protocol (SSL/TLS) and follows the NIST
SP800-57 recommendation to build the internal network protection, avoiding information counterfeiting or man-in-the-middle attacks.The implementation of public key infrastructure (PKI),including the management of certificate application, issuance, extension, and cancellation, etc. and the use of the hardware encryption module to generate the relevant private key can enhance the security level.
To mitigate the impact of network attacks or intrusions on the entire system, the internal network of the MDMS system is partitioned based on the functionality, and the application access network and system management network are physically separated. This kind of isolation can effectively reduce the infected area, and can also be conducive to the rapid recovery services after infection removal.The MDMS system has the security information and event management system (SIEM) and network management system (NMS) to collect a variety logs and events of hardware and software, equipment and customization program and other data sources, to perform big data analysis of real-time malicious behavior, and then to link automation mechanism to timely configuration adjustment, so advanced persistent threat (APT) and other malicious acts can be detected effectively and abnormal compromised devices could be automatically isolated .Host Protection
MDMS system uses the design of host redundancy to ensure the high system availability. The host design is based on the software-defined data center(SDDC) architecture, provides the high elasticity information infrastructure which can automatically expand (shrink) capacity, and all the equipment has the high- availability architecture, in order to avoid the possibility of a single point of failure. The physical and virtual hosts of the MDMS system use the active endpoint protection scheme to protect the system from APT and ransomware intrusion. In addition, the MDMS system regularly handles the security update patching of the whole system software/firmware, and entrusts the professional team with black box tests such as vulnerability scan for vulnerability assessment and penetration test every year, in order to review and strengthen improvements on a regular basis for various security measures.Application Protection
MDMS system uses the full identity access management (IAM) scheme to improve user authentication and authorization of security management. In the human-machine interface, account password has adopted with two-factor authentication, application programming interface (API) access is regulated by an API key or access token, and the mechanism is achieved through the mainstream confederate single sign-on protocol, such as SAML 2.0 and OAuth 2.0, to enhance application access security and avoid the possibility of account password theft. The MDMS system has the user position data synchronization with human resource information system of Taipower, it will automatically disable/remove user account whenever the user position is changed, suspended or user is resigned or retired.Data Protection
For sensitive data, the MDMS system will first apply de-identification (or encrypted) and then store data. Users can obtain restored data, partially shielded data, or de-identifying data according to the authorized rule. The backup principle of the MDMS system is designed to retain at least 3 generations, the system recovery point objective (RPO) is to allow the loss of data within 1 hour after failover, the system recovery time objective (RTO) is within 15 minutes (inclusive) after the failure, and the redundant host shall complete the take-over operation. The disaster recovery exercise and review shall be performed every year to ensure the effectiveness of business continuity management (BCM).
4-3-4 Conclusion
In addition to the security measures described above, Taipower also builds the management mechanism to ensure AMI security measures effectively applied, including the computer room security management, personnel safety management, AMI meter key management, meter program handheld device management, etc. The MDMS system also follows the company’s “Security Incident Emergency Response Plan and Operation Processing Procedures” for event classification, notification channels, etc.
In the future, Taipower will continuously review the technical and regulatory developments of AMI related domain to ensure the timely improvement of the high-level security requirements of the AMI system.